Laparoscopy
The Future of Veterinary Surgery
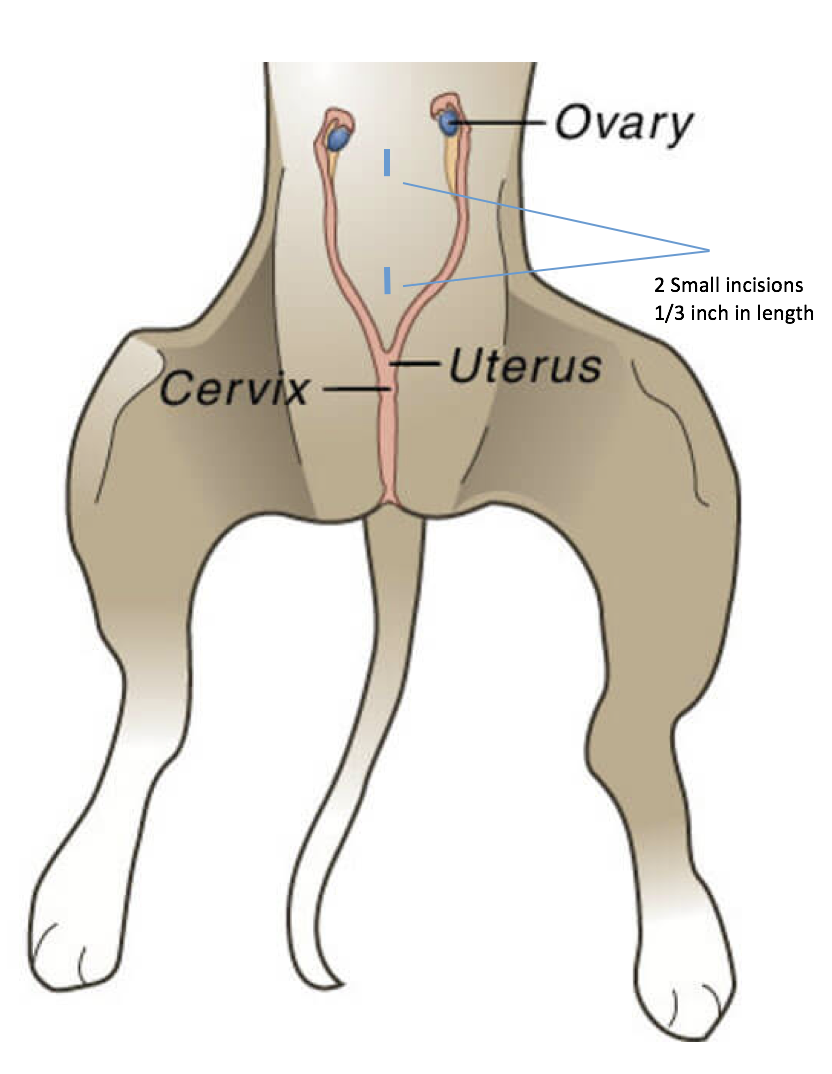
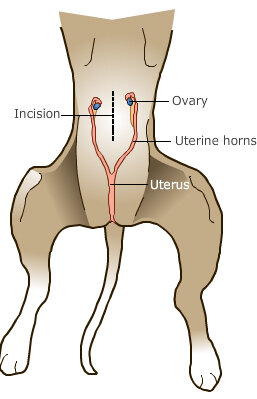
What is a laparoscopic spay?
Dr. Antonio Pedraza believes in minimally invasive procedures is the key for caring and a fast recovery. By performing a spay laparoscopically, the incisions are two tiny holes (1/4 of an inch) in which we will be able to view and access the entire abdomen. The procedure involves removal of the ovaries. Conventional open surgical spaying of female dogs and cats usually involves removal of the ovaries and uterus together (ovariohysterectomy). The key-hole ovariectomy operation is quicker, less involved and less painful than the conventional spay procedure. The ovarian ligament is not torn from the body, but carefully cut and cauterized with virtually no bleeding or pain. No tension is placed on the uterus.
Dr. Pedraza will be able to check the liver, spleen, bladder, kidneys, and the small intestines with his special camera in order to ensure that all organs are functioning correctly. Activity restriction is only recommended for the first 2-3 days after a laparoscopic spay versus 14 days for a traditional spay.
The Future of Veterinary Surgery
What is a laparoscopic spay?
Dr. Antonio Pedraza believes in minimally invasive procedures is the key for caring and a fast recovery. By performing a spay laparoscopically, the incisions are two tiny holes (1/4 of an inch) in which we will be able to view and access the entire abdomen. The procedure involves removal of the ovaries. Conventional open surgical spaying of female dogs and cats usually involves removal of the ovaries and uterus together (ovariohysterectomy). The key-hole ovariectomy operation is quicker, less involved and less painful than the conventional spay procedure. The ovarian ligament is not torn from the body, but carefully cut and cauterized with virtually no bleeding or pain. No tension is placed on the uterus.
Dr. Pedraza will be able to check the liver, spleen, bladder, kidneys, and the small intestines with his special camera in order to ensure that all organs are functioning correctly. Activity restriction is only recommended for the first 2-3 days after a laparoscopic spay versus 14 days for a traditional spay.
What is the difference?
Laparoscopic Spay Vs.
2 Tiny Incisions (Holes) - 1/4in to 1/2in
Reduced pain due to precise surgical cuts
Up to 65% less post-operative pain
Minimally invasive technique reduces chance of infection
Pet will be able to return to normal activity faster - very important for very active or larger breeds.
Traditional Spay
5-10 Cm Incisions
Pain and bruising from blindly tearing ovarian ligament
Post-Operative Pain more significant
Open Surgical procedure
Recovery is usually three weeks with limited activity